Identify Stroke Symptoms
See That Stroke Coming
A stroke is a medical condition in which the brain cells die because of the lack of oxygen. The patient may lose speech, there could be a problem with memory, or one or both sides of the body can become paralyzed.
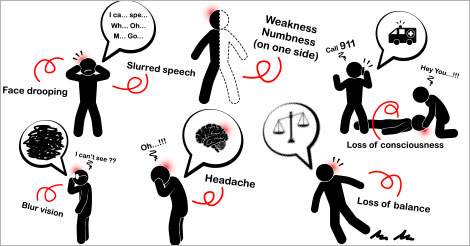
Use the FAST method to recognize the symptoms:
- F(face) - uneven smile, facial droopiness, vision disturbance or numbness
- A (arm and leg) - difficulty walking, or weakness
- S (speech) - slurred, incoherent and inappropriate words
- T (time) -If you notice any of the above symptoms, immediately seek help.
Remember that TIME is critical. The more time you lose in getting medical help, the more cells die in your brain.
Now, we all know that a healthy lifestyle including quitting smoke, limiting alcohol, eating plenty of fruits and veggies and keeping weight, blood pressure and sugar in control can lower the likelihood of having a stroke. Still, there are some lesser-known ways to protect and keep the stroke at bay.
Walk, walk, walk
Walk at least 20 minutes a day. One can even break it into two 10- minute sessions. Walk briskly but steadily. Don’t stop to in between too often.
Recognise when you feel low
Know the difference between your feeling of sadness and state of depression. Sadness is usually temporary, while depression can be a prolonged condition. Have a heart to heart with your doctor if you feel persistently sad, anxious, irritable, helpless, or a sense of ‘emptiness’ or ‘guilt’, looms you.
Mind your migraine
Migraine (a type of headache) appear to be linked with stroke risk in women. Though there’s no clear explanation for the interlinking of both but treating migraines may reduce the chances of getting a stroke.
Monitor irregular heartbeats
Don’t ignore the palpitations or irregular heartbeats if you feel, especially if the heart fluttering occurs with shortness of breath, light headedness and chest pain. An abnormal heartbeat enhances risk of stroke manifold.
Eat potassium rich food
Eat more foods like sweet potatoes, raisins, bananas and tomatoes as all of them are loaded with potassium. Researchers say a diet full of in potassium rich foods may reduce stroke risk by almost 20%. More rich food sources of potassium are fruits and veggies, fish, poultry and dairy products.
Lengthen that short fuse
Angry and aggressive people may be at a higher risk of getting a stroke. Keep the cool and practice patience. Aggression and anger is anyways not good for mental, physical and emotional state of the body.
Several studies have demonstrated that a high percentage of stokes can be easily prevented. Through regular preventive health checkups, clots and narrowing of cranial vessels can be identified and action can be taken to correct the abnormality in time.
.